The joy of supporting PXE-boot in a number of different environments have created a mental note-to-selflist when operating PXE with Configuration Manager. These are my notes, and if they can be of use to anyone else – thats great.
Overview
PXE-boot and its dependencies on operational and a managable network is key and therefore a basic understanding is vital. Coretech has published a great overview explaining PXE and its relationship with DHCP.
Basic setup
Some minor tweaks to get started are of course required even for the not-so-complex environment and 4SysOps has a great guide that details the generic troubleshooting steps on basic configuration.
In essence:
- An operational Configuration Manager environment is key
-
- A Distribution Point for the Configuration Manager site that is setup to handle PXE
- A possibility to handle the broadcast requests when pressing F12 on the client
-
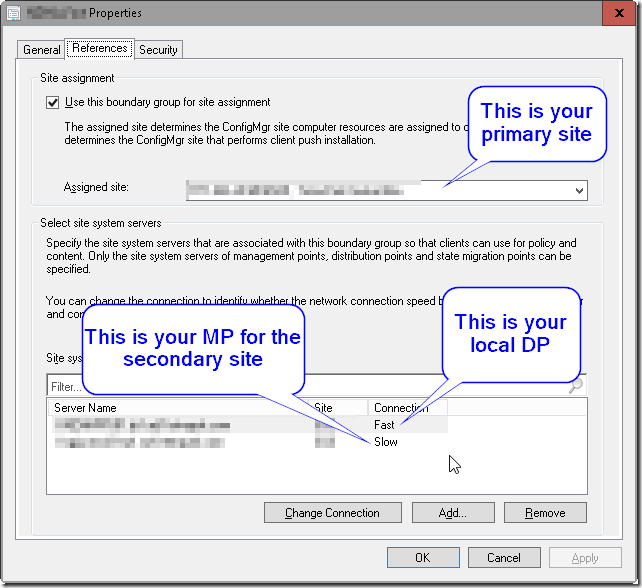
The last part (handle broadcast requests) is normally something that is managed by a network operations-team. There are of course (why should there be one?) many different ways to configure this and normally the discussion stands between DHCP Options (not supported by Microsoft) or IP-helpers. TechThoughts has an overview with detailed pros and cons, however clearly states that IP-helpers is the way to go forward.
Challenges
Once you get everything setup – here comes a list in order of likely hood to cause you issues.
What does a client see when pressing F12?
Well, you see on the screen that you pressed F12 and potentially some sort of diagnostic information is presented to you. Is this information useful? Complete? Of debugging-quality?
Most likely not! There are two tools available – one from Citrix (PXEChecker) and one from 2pint (powershell) – which provides great insight into what shows up at your client.
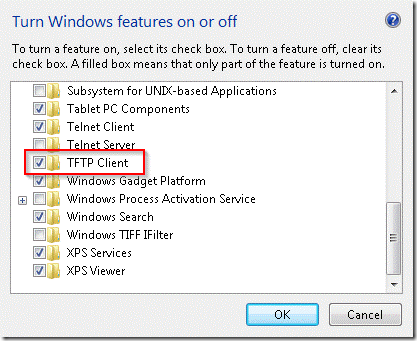
Test TFTP download
Wondering if you have a responsive PXE-server? Follow the previous guide howto test the download of a file
DNS and PXE
As PXE and its reliance on just ip-addresses is heavy – the first question that comes to mind is why DNS is a thing? Well, legacy servers (still supported for the role of Distribution Point) that run Windows Server 2008 R2 may exhaust the available ports if DNS and PXE-role is hosted on the same system.
Resolve the issue by configuring Windows Deployment Services to dynamically request and allocate ports that are available.
Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WDSServer\Parameters
DWORD: UDPPortPolicy
Value: 0
PXE and DHCP
If the Distribution Point (with PXE enabled) and the DHCP-server is configured on the same server a few technical configurations are required. Normally these are set up properly, however it can always be a good thing to double-check.
Configure WDS to not use the same ports as DHCP
Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WDSServer\Providers\WDSPXE
DWORD: UseDHCPPorts
Value: 0
Configure the DHCP-server to set option 60. Option 60 is intended for the client to know that in addition to the server providing an answer to the request for IP-address, a PXE-server also operates on the same server.
Command-line:
WDSUTIL /Set-Server /UseDHCPPorts:No /DHCPOption60:Yes
It’s slow
ConfigMgr has gradually provided improved ways to make PXE-boot go faster. CCMExec wrote article on howto tweak the configuration for boot-times (RamDiskTFTPBlocksize and RamDiskTFTPWindowSize). The sweetspot seems to be at 16384 / 8
Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\DP
DWORD: RamDiskTFTPWindowSize
Value: 8
DWORD: RamDiskTFTPBlockSize
Value: 16384 (1456 allows for higher compatibility)
It starts to download but freezes (0xC0000001)
If the error is prevalent and not related to a specific device or model – most likely this relates to issues with something between the server and the client not beeing able to handle the default size of 1456 in block size. Windows Server 2003 was set to use a block size of 512, and since Windows Server 2008 this was bumped to 1456. If this fails – set it to 512 and verify compatibility. Previously the possibility was tested with 1432 and some success has been confirmed.
Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\WDSServer\Providers\WDSTFTP
DWORD: MaximumBlockSize:
Value: 512 (or 1432)